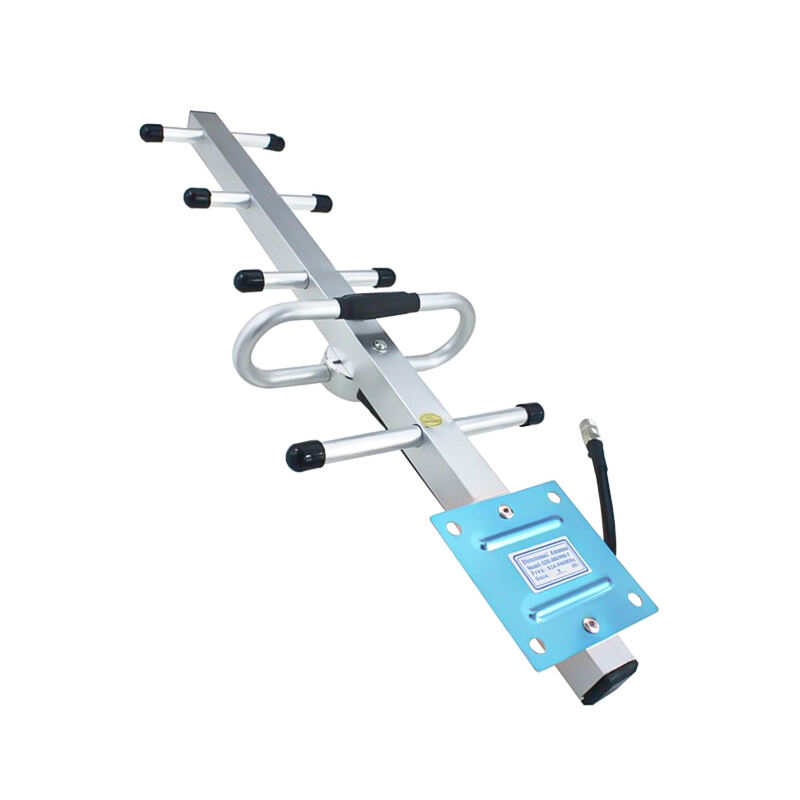
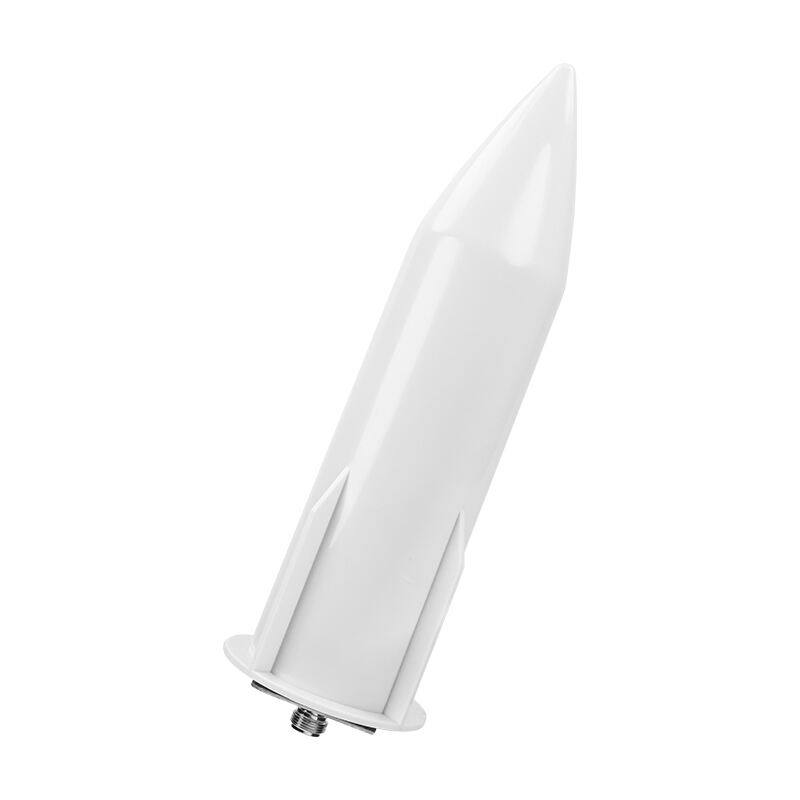
omni vs directional antenna
Omni and directional antennas represent two distinct approaches to wireless signal transmission and reception. Omnidirectional antennas broadcast signals in a 360-degree pattern horizontally, making them ideal for applications requiring widespread coverage. These antennas emit radio waves in all directions, similar to a light bulb illuminating a room. In contrast, directional antennas focus their signal strength in a specific direction, much like a spotlight. They concentrate the radio frequency energy into a narrower beam, providing increased range and signal strength in the targeted direction. The technology behind these antennas involves different radiation patterns and gain characteristics. Omnidirectional antennas typically have lower gain but offer broader coverage, while directional antennas provide higher gain in a specific direction. Common applications for omnidirectional antennas include WiFi routers in homes and offices, mobile phone base stations, and public broadcasting systems. Directional antennas are frequently used in point-to-point communications, satellite dishes, and long-range wireless networking. The choice between these antenna types depends largely on the specific use case, coverage requirements, and environmental factors.